- F = − kx
- where
- F is how much push or pull is on the spring (e.g. 10 kilograms)
- k is the spring constant, or how strong the spring is. Different springs have different strengths or k.
- x is how far the spring was pushed or pulled
- The negative sign is because the direction of the force is always opposite of the direction that the spring was pushed or pulled. When x = 0, the spring how far it was when there was no push or pull on it. The spring is at the equilibrium position. There is a minus sign because the force of the spring does not go to the same direction as the spring moves. This equation only works on a linear spring. A linear spring is a spring that is only being pushed or pulled in one direction, like left or right or up or down.
Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy is the energy saved in an object that is stretched, compressed (compression is pressing objects together), twisted or bent. For example, an arrow gets the elastic potential energy from the bow. When it leaves the bow, the potential energy turns into kinetic energy. The equation of the elastic potential energy is: 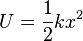
- where
- U is the elastic potential energy.
- k is the spring constant.
- x is the distance pushed or pulled.
2010年12月30日星期四
The spring equation
the length of a spring always changes by the same amount when it is pushed or pulled. The equation for that is:
订阅:
博文评论 (Atom)
没有评论:
发表评论