For one particle that only moves in one direction other than time, the Schrödinger equation looks like:
where:
- i is the square root of minus one
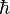 is the reduced Planck's constant
is the reduced Planck's constant- t is time
- x is a place in space
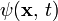 is the wavefunction
is the wavefunction is the Hamiltonian energy operator
is the Hamiltonian energy operator
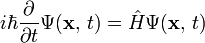
没有评论:
发表评论